Your lender calculates a set monthly payment based on the loan amount, the rate of interest, and the variety of years need to settle the loan. A longer term loan causes higher interest expenses over the life of the loan, successfully making the home more pricey. The rate of interest on variable-rate mortgages can change at some time.
Your payment will increase if interest rates go up, but you might see lower needed month-to-month payments if rates fall. Rates are generally fixed for a variety of years in the start, then they can be adjusted each year. There are some limitations as to how much they can increase or reduce.
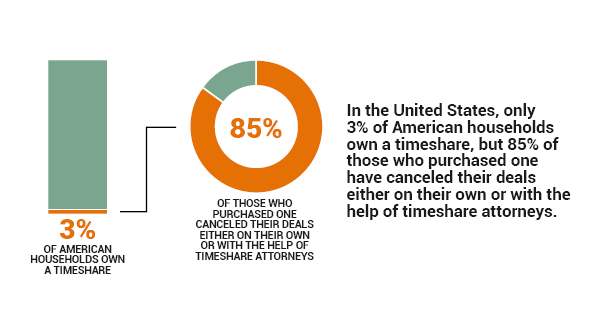
Second mortgages, likewise understood as home equity loans, are a method of borrowing versus a home you already own. You might do this to cover other expenses, such as debt consolidation or your kid's education expenditures. You'll include another mortgage to the home, or put a brand-new very first mortgage on the house if it's paid off.
They only receive payment if there's money left over after the very first mortgage holder earns money in case of foreclosure. Reverse mortgages can provide earnings to homeowners over the age of 62 who have actually developed equity in their homestheir residential or commercial properties' worths are substantially more than the remaining home loan balances versus them, if any. In the early years of a loan, most of your home mortgage payments approach settling interest, making for a meaty tax reduction. Much easier to certify: With smaller sized payments, more borrowers are eligible to get a 30-year mortgageLets you money other objectives: After home mortgage payments are made every month, there's more money left for other goalsHigher rates: Due to the fact that lending institutions' danger of not getting repaid is spread out over a longer time, they charge greater interest ratesMore interest paid: Paying interest for 30 years adds up to a much higher overall expense compared with a shorter loanSlow growth in equity: It takes longer to build an equity share in a homeDanger of overborrowing: Getting approved for a https://www.scribd.com/document/475253234/389123how-can-i-sell-my-timeshare bigger home loan can lure some people to get a bigger, better house that's more difficult to manage.
Higher maintenance expenses: If you opt for a pricier house, you'll face steeper expenses for real estate tax, upkeep and perhaps even energy costs. "A $100,000 house might require $2,000 in yearly upkeep while a $600,000 house would need $12,000 annually," states Adam Funk, a licensed monetary organizer in Troy, Michigan.
With a little preparation, you can integrate the safety of a 30-year home mortgage with one of the primary advantages of a much shorter home mortgage a quicker course to totally owning a home. How is that possible? Settle the loan faster. It's that basic. If you wish to attempt it, ask your loan provider for an amortization schedule, which reveals how much you would pay each month in order to own the home completely in 15 years, twenty years or another timeline of your picking.
Making your home mortgage payment immediately from your savings account lets you increase your month-to-month auto-payment to meet your objective however override the boost if necessary. This approach isn't similar to a getting a much shorter mortgage because the interest rate on your 30-year home loan will be slightly higher. Rather of 3.08% for a 15-year fixed home loan, for example, a 30-year term might have a rate of 3.78%.
For home loan consumers who want a shorter term however like the flexibility of a 30-year mortgage, here's some suggestions from James D. Kinney, a CFP in New Jersey. He advises purchasers gauge the monthly payment they can manage to make based on a 15-year home mortgage schedule but then getting the 30-year loan.
Whichever way you pay off your house, the most significant benefit of a 30-year fixed-rate home loan may be what Funk calls "the sleep-well-at-night impact." It's the warranty that, whatever else changes, your home payment will remain the very same.
Purchasing a house with a mortgage is probably the biggest monetary deal you will participate in. Normally, a bank or home loan lender will finance 80% of the price of the house, and you accept pay it backwith interestover a specific period. As you are comparing lenders, mortgage rates and alternatives, it's practical to comprehend how interest accumulates each month and is paid.
These loans featured either fixed or variable/adjustable rates of interest. Many home loans are completely amortized loans, meaning that each month-to-month payment will be the very same, and the ratio of interest to principal will alter with time. Merely put, on a monthly basis you pay back a part of the principal (the amount you have actually borrowed) plus the interest accumulated for the month.

The length, or life, of your loan, also determines how much you'll pay monthly. Totally amortizing payment describes a routine loan payment where, if the customer pays according to the loan's amortization schedule, the loan is totally paid off by the end of its set term. If the loan is a fixed-rate loan, each completely amortizing payment is an equivalent dollar amount.
Extending out payments over more years (as much as 30) will normally result in lower month-to-month payments. The longer you require to pay off your mortgage, the greater the overall purchase cost for your house will be because you'll be paying interest for a longer period. Banks and lenders mostly offer two kinds of loans: Interest rate does not alter.
Here's how these operate in a home mortgage. The regular monthly payment remains the very same for the life of this loan. The rate of interest is locked in and does not change. Loans have a payment life expectancy of thirty years; shorter lengths of 10, 15 or twenty years are also typically available.
A $200,000 fixed-rate mortgage for thirty years (360 month-to-month payments) at a yearly rate of interest of 4.5% will have a regular monthly payment of roughly Have a peek at this website $1,013. (Taxes, insurance and escrow are extra and not included in this figure.) The yearly interest rate is broken down into a month-to-month rate as follows: An annual rate of, state, 4.5% divided by 12 equals a monthly rate of interest of 0.375%.